Atoms
%20sculpture.jpg)
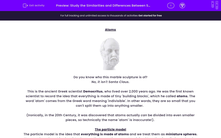
Do you know who this marble sculpture is of?
No, it isn't Santa Claus.
This is the ancient Greek scientist Democritus, who lived over 2,000 years ago. He was the first known scientist to record the idea that everything is made of tiny 'building blocks', which he called atoms. The word 'atom' comes from the Greek word meaning 'indivisible'. In other words, they are so small that you can't split them up into anything smaller.
(Ironically, in the 20th Century, it was discovered that atoms actually can be divided into even smaller pieces, so technically the name 'atom' is inaccurate!).
The particle model
The particle model is the idea that everything is made of atoms and we treat them as miniature spheres. You may have learnt in chemistry lessons that more than one atom joined together is called a molecule.
In physics, we use the term 'particle' to mean either atoms or molecules, so it is a general word for very small pieces of matter.
You need to know that solids, liquids, and gases are the three states of matter, and you also need to have an understanding of how the particles in each of these states behave.
Solids

The particles in solids are packed very close together, meaning solids have a very high density. The arrangement of the particles in rows and columns is called a lattice. They each vibrate about a fixed position and the forces between the particles are very strong.
Liquids

The particles in a liquid are further apart and the forces between them are weaker. Instead of vibrating about fixed positions, the particles in a liquid move randomly. Fluids can fill the shape of any container as the particles are able to slide over each other. Notice that each particle is still in contact with another particle.
Gases

Finally, gas molecules are the fastest moving. Gases are the least dense state of matter as their particles are so far apart. They have very weak forces between them, and they also move randomly in all directions. Just like liquids, they can fill the shape of any container.
Now you know the difference between the three states of matter, you are ready to try some questions!