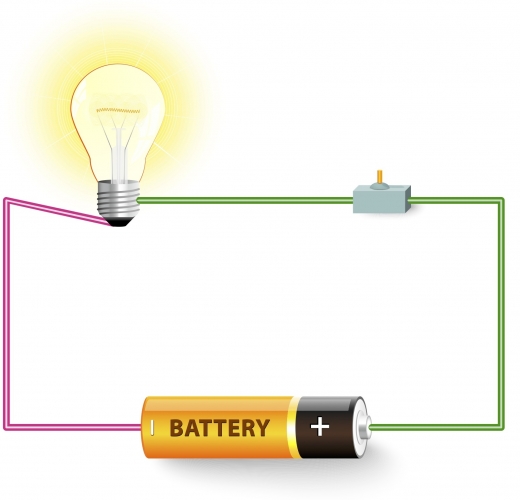
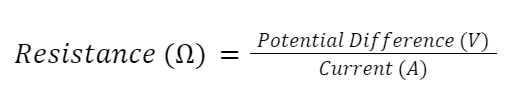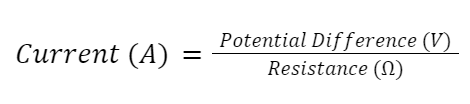Let's imagine building a simple circuit with a bulb, a battery and a switch.
What if we added a second bulb, next to the first? The current in the circuit would decrease. That's because the second bulb adds more resistance to the circuit.
Let's learn about resistance in circuits!
Electrical circuits are made up of different components (parts like bulbs, buzzers, etc). All of these components provide a different amount of resistance.

Resistance is a measure of how much something reduces the flow of current in a circuit. The greater the resistance of a component, the lower the current passing through it.
Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω). Different components in a circuit have different resistances.
Resistance can be calculated using this equation:
Here is an example.
Imagine that same circuit from the start of this activity.

The current in the circuit is 1.5 Amps. The potential difference measured across the bulb is 4.5 Volts.
What is the resistance of the bulb?
Resistance (Ω) = 4.5 V ÷ 1.5 A
Resistance = 3 Ω
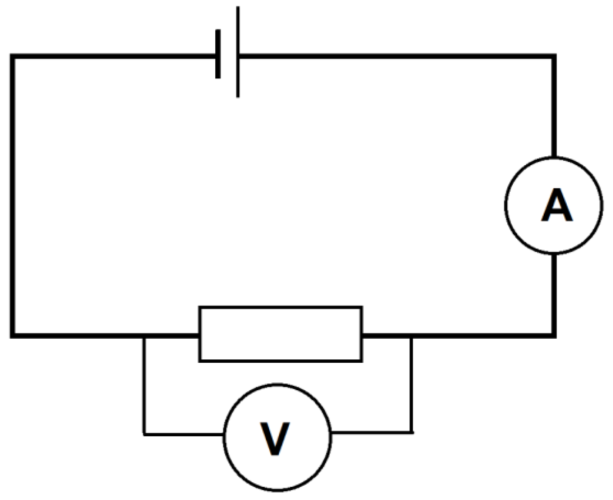
In an experiment, we can find the resistance of a component in a circuit by measuring the current in the circuit, and the potential difference across the component.
In the circuit diagram here, we can see an ammeter in the same loop as the other components, to measure the current.
We can see a voltmeter in a parallel loop around the component we want to investigate. This measures the potential difference.
Using this data, we could calculate the resistance of the component.
The resistance equation can be used in other ways too. We can rearrange the equation to help us calculate current, or potential difference.
Potential Difference (V) = Current (A) × Resistance (Ω)
Let's try another question.
In a circuit, a bulb has a resistance of 12 Ohms. The current through the bulb is 0.8 Amps.
What is the potential difference across the bulb?

First, let's identify the right equation to use. We need to calculate the potential difference, so let's use this one:
Potential Difference (V) = Current (A) × Resistance (Ω)
Potential difference (V) = 0.8 A × 12 Ω
Potential difference = 9.6 V
As you can see from this example, the greater the resistance, the greater the potential difference across the component. In other words, components with a high resistance transfer a greater amount of electrical energy.
Now let's try some questions!
Remember that you can come back to this page at any point by clicking the red help button on the screen.