In the topic of electricity, we use a wide range of symbols to represent circuit components. Let's learn about some more of the interesting components that we can use in circuits!
Below is a list of some of the circuit symbols we use in physics. These symbols are used internationally so that anyone can understand any circuit diagram.
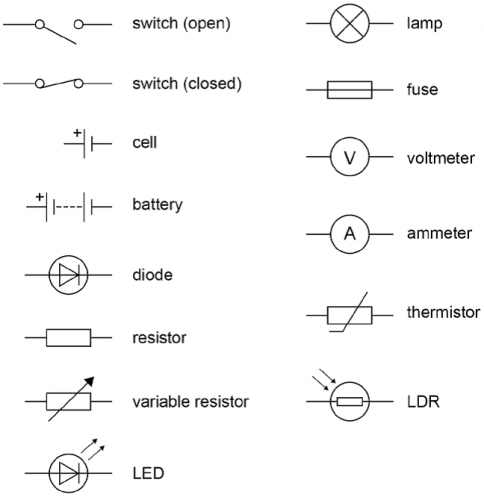
You might be familiar with some of these symbols but there are others you may not have seen before. Let's learn about some of them.
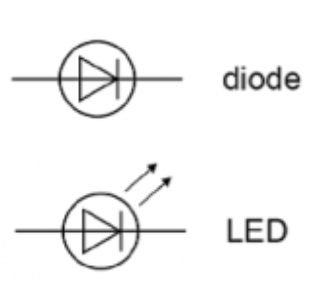
Diode and Light Emitting Diode (LED)
A diode is a component that only allows electricity to flow in a circuit in one direction.
If the diode is oriented as in the image above, it allows electricity to flow from left to right but prevents it from flowing from right to left.
A light-emitting diode (LED) also allows electricity to only flow in a circuit in one direction. It also emits light when electricity flows through it. LEDs have many uses, for example, the red light in your remote control.
Thermistor
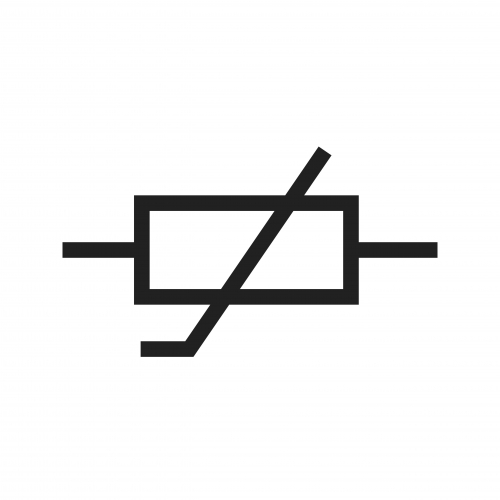
A thermistor is a type of resistor. Generally, resistors reduce the flow of current in a circuit. They are represented with a rectangle as an electrical symbol. This variation, the thermistor, has a resistance that varies with temperature. Depending on the type, it might have a low resistance at a high temperature, and a high resistance at a low temperature.
Thermistors are useful in sensing circuits, like in heating systems in homes. If the temperature gets too cold, the resistance in the circuit changes, and this can be used to trigger turning the heating on.
Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
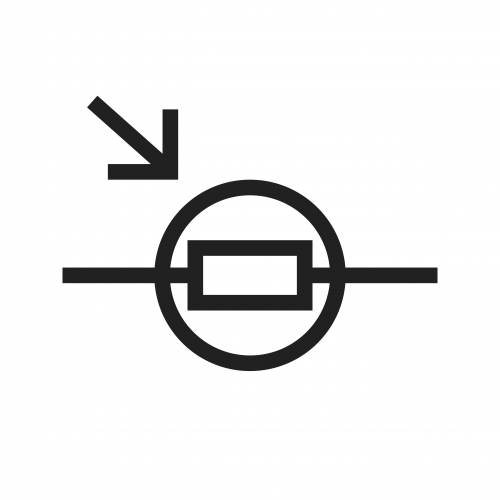
A light-dependent resistor (LDR) works in a similar way to a thermistor. The brightness of the light on the LDR affects the resistance. LDRs can be used in sensing circuits - for example, in street lights. When it gets dark, the light on the LDR reduces, and the change in resistance can be used to trigger the street light turning on.

Fuse
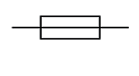
A fuse is often used as a safety feature in a circuit - they are used in many of the plugs we use in our homes. The fuse has a filament inside (a thin piece of wire).
If the current in the circuit is too high, that's often a sign of an electrical problem like a short circuit. This could cause a fire. A fuse prevents this because when the current in the filament is high, the filament gets hot, and melts.
This breaks the circuit, making it safe.

Here is an example of a circuit diagram that uses some of these components.
Here, the electricity flows from the cell towards the right (in the direction of the arrow). The current flows through the diode on the right. If the diode was the other way around, the electricity would not flow.
The current then flows through a thermistor. A voltmeter is connected in its own loop (parallel) to the thermistor.
Phew - that's a lot to take in!
Let's try some questions, but remember that you can come back to this page at any point by clicking the red help button on the screen.