Did you know that a smartphone has more than 9,000 times more germs than a toilet seat?! Gross!
So what are germs? Germs often are referred to as microorganisms. Microorganisms are just that - organisms that are microscopic. Most microorganisms are harmless, however, some aren’t. Organisms that cause infectious diseases are called pathogens. There are different types of pathogens: bacteria, fungi, viruses and protists.
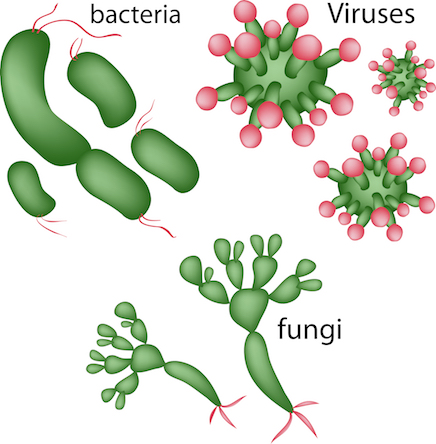
Some diseases are communicable - they can be spread from organism to organism. Different pathogens spread in different ways. Some spread through direct contact, such as in bodily fluids (like blood) or through sex. Other pathogens spread through water or air, or in food.
Pathogens cause illness in three main ways:
Toxins: Toxins are harmful substances produced by the pathogen that poison the body’s tissues and enzymes. This makes us feel ill.
Reproduction: Bacteria and viruses may reproduce inside the body. A rise in the number of pathogens can damage a cell, even causing it to burst. Some pathogens hijack resources that the cell needs to be able to survive.
Immune response: Sites of infection often become swollen, sore and hot as a result of increased blood flow, often making us feel rotten.
Let’s take a look at these disease-causing pathogens in more detail!
Viruses
Viruses are the smallest pathogens. The genetic material of a virus is injected into the host cell. It then takes over the host cell by copying its DNA hundreds and thousands of times. The host cells eventually burst.
Some examples of viruses are measles, HIV and tobacco mosaic virus (TMV). Let's explore these further:
| Name |
Measles |
HIV |
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) |
| Description |
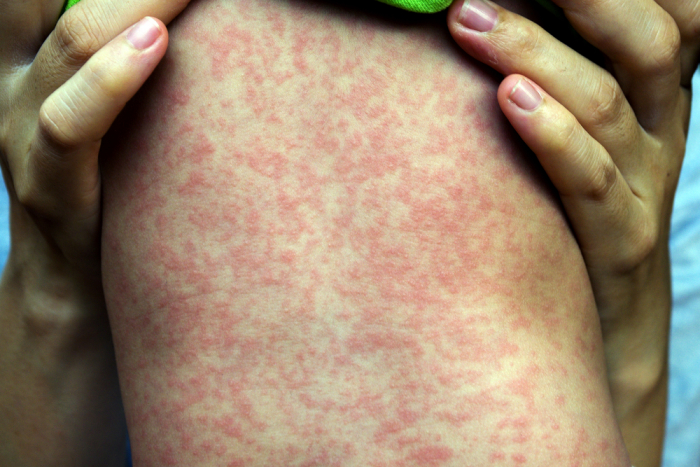
Measles can cause complications, especially in young children which is why they are often vaccinated against it.
|
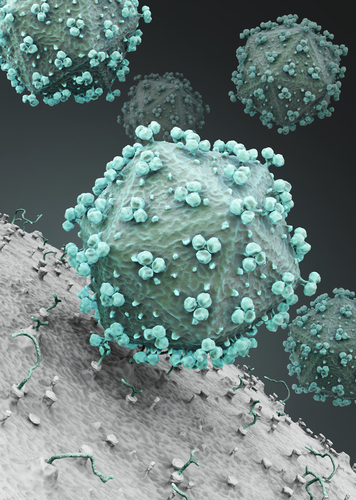
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. HIV sufferers might not know they are infected as symptoms may pass. However, the virus can cause the immune system to become so damaged that it can’t deal with other infections - this is called AIDS. |
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) affects many species of plants, for example tobacco, tomato, peppers. It affects chloroplasts and causes a discolouration on leaves of plants which will affect the growth of the plant.
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Symptoms |
Fever, skin rash, cold-like symptoms |
Flu-like illness |
Discolouration on leaves of plants |
|
Spreads |
Inhalation of droplets from sneezes and coughs |
Through bodily fluids like blood, often when drug users share needles or by sexual contact |
Spreads through direct contact and contaminated seeds |
Bacteria
Bacteria are larger than viruses. Bacteria replicate and divide very rapidly, allowing them to spread quickly.
|
Name |
Salmonella |
Gonorrhoea |
Crown gall disease |
| Description |
Salmonella causes food poisoning. |
Taking antibiotics or using contraception such as condoms during sexual contact can prevent spreading. |
Infects plants and fruits, such as grapes, nuts |
| Symptoms |
Abdominal cramps, vomiting and diarrhoea |
Causes a burning pain when urinating, thick discharge from the vagina or penis. |
Causes galls or swollen tissues to grow on the plant stems or roots, preventing growth. |
| Spreads |
Bacteria in food or food prepared in unhygienic conditions |
Sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by a bacterium |
Contaminated soil, water and farming tools |
Fungi
Fungi come in different shapes and sizes. Some are microscopic, whereas others are quite large. Fungi have lots of uses in industry.
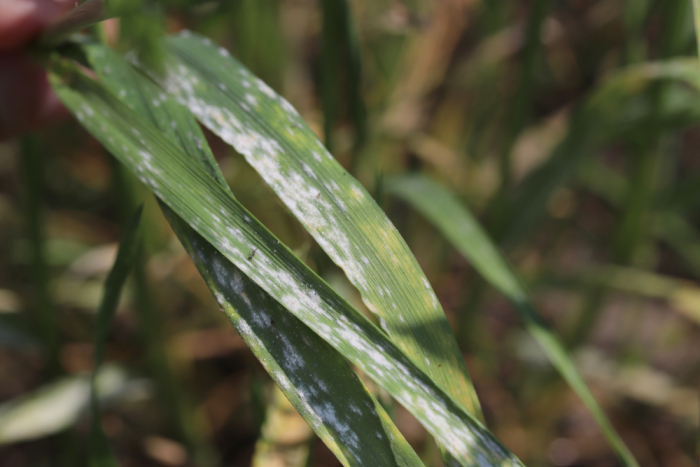
| Name | Rose black spot | Barley powdery mildew |
| Description |
Caused by a fungus which infects roses. Affects the growth of the plant as photosynthesis is reduced. |
Affects barley crops and the fungus can multiply quickly. |
|
Symptoms |
Purple or blacks spots develop on leaves, which turn yellow |
Yellow spots, white fluffy growth on leaves and stems |
|
Spreads |
Air or water, as well as through direct contact by gardeners |
Fungal spores are spread in the air by the wind. |
Protists
Protists are usually microscopic and vary greatly from one another.
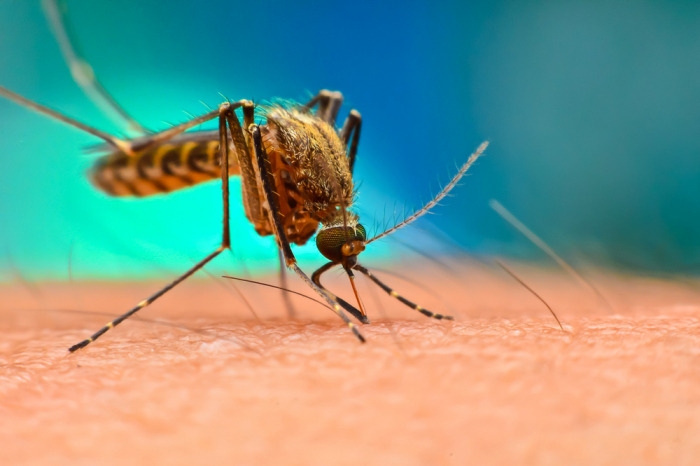
| Name | Malaria |
|
Description |
Malaria is spread by mosquitos which carry the plasmodium protist. Mosquitos suck blood containing the protists from an infected person. Infection can only be prevented by stopping individuals from being bitten. People sleep under mosquito nets and wear insect repellent to avoid bites.
|
|
Symptoms |
Fever, sweats and chills, headaches, vomiting and diarrhoea |
|
Spreads |
They pass the protist to other people they suck blood from. The mosquitos do not become ill and are called 'vectors' because they transmit the disease. |
In the following activity, you will look at how pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, fungi and protists cause a variety of diseases.