In this activity, we will be learning how to describe translations.
Translations are when shapes are moved on a coordinate grid.
They are not rotated or reflected, just moved.
They will stay the same size and shape.
Here is an example.
Look at the following L-shapes drawn on x and y-coordinate axes.
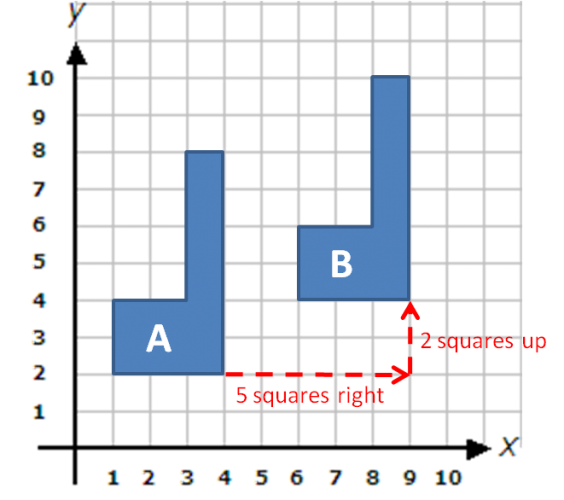
Shape A has been translated, or shifted, to land on Shape B.
This has been done by moving each point 5 squares to the right and 2 squares up.
We can write this instruction as R5, U2.
Let's try an example question ourselves.
Example
How is Shape B translated, to land on Shape A?
Answer
This has been done by moving each point 5 squares to the left and 2 squares down.
We can write this in a shorthand version as L5, D2.
Look at the diagram below, which shows the transition clearly.

Remember that in translations, the shapes are not rotated or reflected.
They stay the same way up, but just in a different place on the grid.
Let's take a look at some questions.







