Lots of things jumbled up together make a mixture.
For example, sea water is a mixture - if we took a sample of it we would find that it contained water, salt, sand and seaweed.
It would be easy to separate the salty sea water from the sand and seaweed by a method called filtration. That's because the sand and sea weed are solids.
The diagram illustrates how filtration is done in a scientific laboratory.
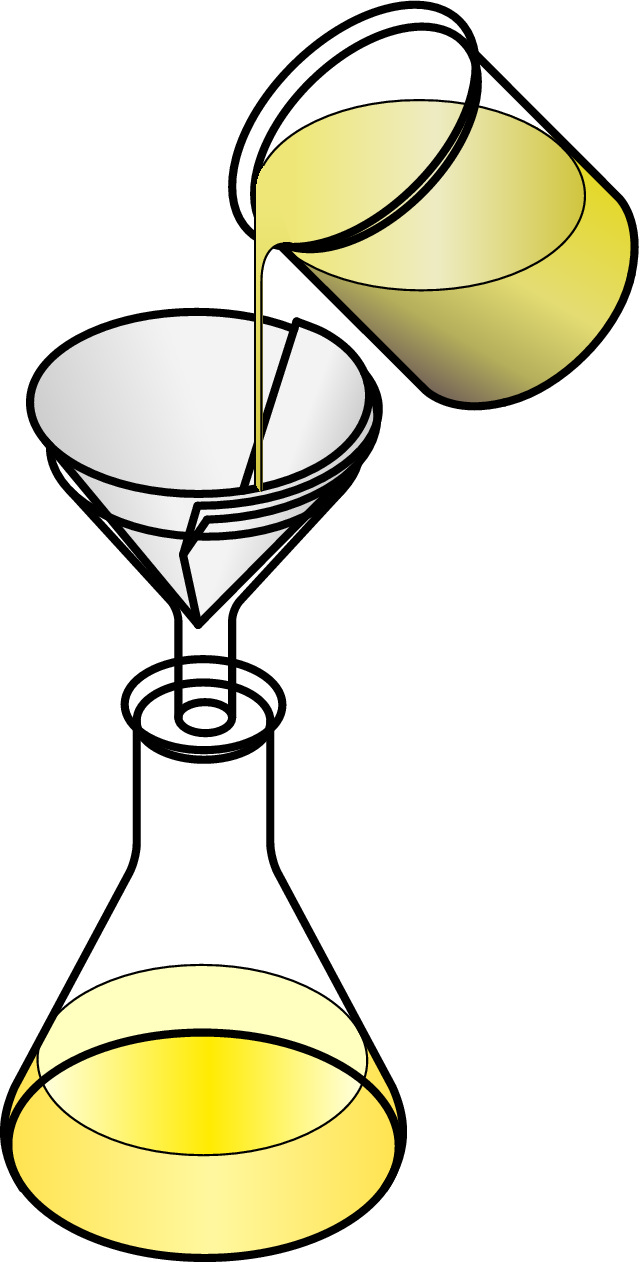
Filter paper is placed in a funnel and placed above something to catch the liquid in. The mixture is poured into the filter paper. The solid part of the mixture is caught in the filter paper. The liquid runs through the filter paper into the container.
The salty seawater would be separated from the sand and seaweed because sand particles are too big to go through the filter paper and seaweed comes in big chunks.
Salt particles, on the other hand, do not get trapped in the filter paper. That's because salt is dissolved in water and the two of them make a solution. Substances that make solutions cannot be separated by filtration.
In the case of the sea water solution, salt on its own can only be obtained if the water is left to evaporate. During evaporation, the water turns into a gas leaving solid salt crystals behind.
.jpg)
Are you ready to begin the questions on filtration and evaporation?








