Coal, oil and natural gas are known as fossil fuels. They are incredibly important to us because they provide us with the energy we need to power our cars, heat our homes and cook our food.



They are known as fossil fuels because they were formed from dead plants and animals kept under pressure for millions of years.
These fossil fuels can also be classed as hydrocarbons because they are made of only two elements - hydrogen and carbon.

When hydrocarbons are burned, oxygen from the air will combine with each of the elements in the hydrocarbon (that's combustion).
For example, we can take the burning of the hydrocarbon methane (which is the main constituent of natural gas). The carbon will combine with oxygen from the air to form carbon dioxide, and the hydrogen oxidises to form water. This is true of all hydrocarbons.
The products of combustion of hydrocarbons can be tested in the lab using the equipment shown below:
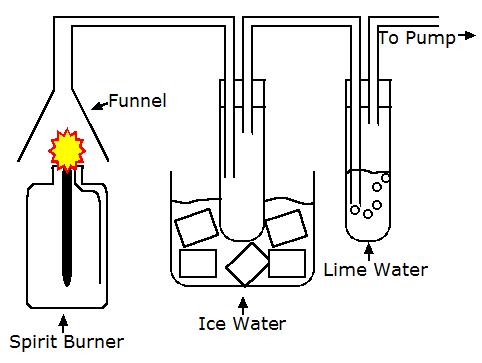
When the fuel, like alcohol, in the spirit burner is burning, the water vapour produced condenses and turns back into liquid water when it passes through the beaker of ice. The carbon dioxide produced from the fuel's combustion reacts with the limewater, turning it from colourless to milky white.
Many of these fuels, however, can contain sulfur as an impurity. If sulfur is present, the acidic gas sulfur dioxide will also be produced. This gas is the major contributor to the acidification of rainwater better known as acid rain.
There's lots to remember here - you can look back to the introduction at any point during the activity by clicking on the red Help button at the side of the screen.
Let's get started!