Electrical circuits use components for different functions.
A good example is a bulb - this is a component that transfers electrical energy into light energy in a circuit.

A common component in electrical circuits is the resistor. But what are resistors? What are they used for? Let's find out!
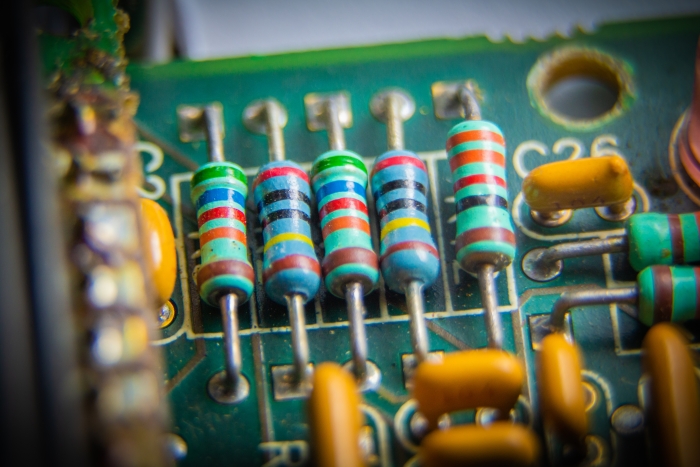
You can see resistors in the image above. Standard resistors are cylindrical and have different bands of colours across them.
To understand resistors, we will start by understanding the concepts of current and resistance in circuits.
The current in a circuit tells us how quickly electrical charge is being transferred in a circuit. Current is measured in amps, using an ammeter.
Every component in a circuit (like a bulb, for example) has resistance. Resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for the electrical current to flow through the component.

The more resistance a component has, the lower the current.
The lower the resistance, the higher the current.
Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω).
So, what are resistors?
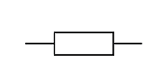
The image above is the circuit diagram symbol for a fixed resistor. The resistor has a specific resistance, for example, 15 Ω.
The purpose of the resistor is to reduce the current flowing in a circuit.
This is because it is often important to control the current in a circuit. For example, adding a resistor in series with a bulb will reduce the brightness of the bulb.

The different coloured bands are used to show the amount of resistance of a resistor, in Ohms.
So far we have looked at fixed resistors, but there are other kinds of resistors too.
Variable resistor:
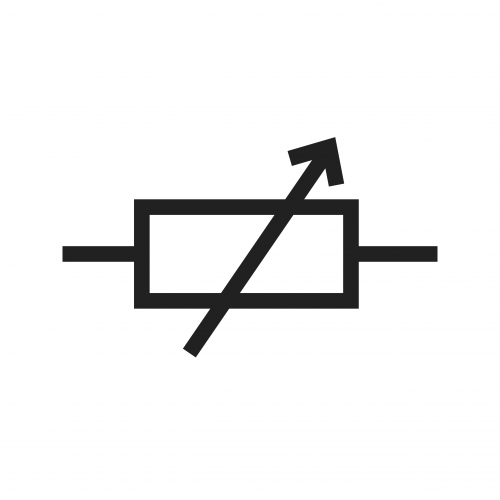
A variable resistor is a type of resistor that the user can control, increasing or decreasing the resistance. This can be useful when you want to make changes to the current in the circuit.
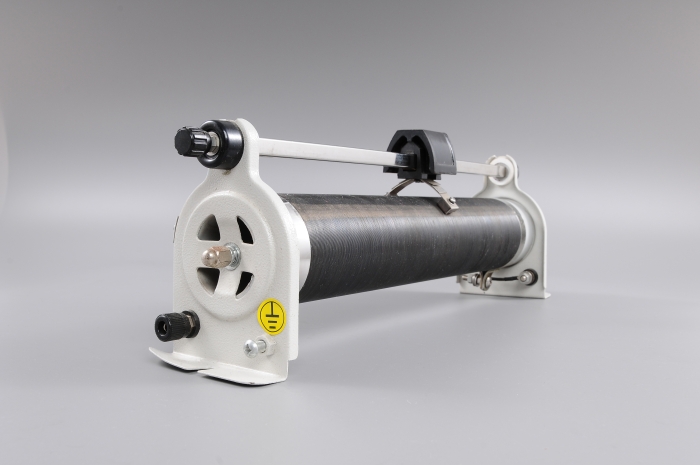
There are different types of variable resistor but they all work in a similar way. A common version of a variable resistor is shown below.

Light-dependent resistor:
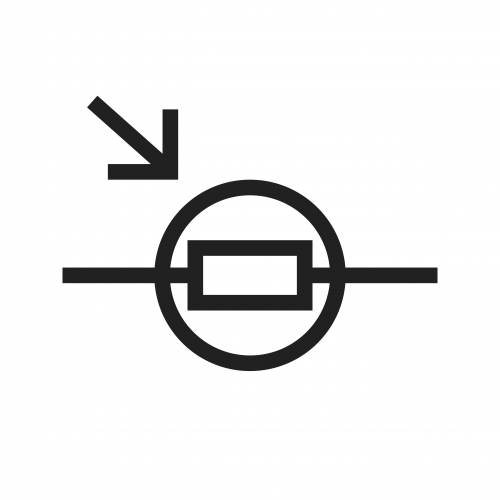
The resistance of a light-dependent resistor varies as the light falling on it varies. This is useful in circuits where we want the current to change depending on the light level, e.g. street lights.
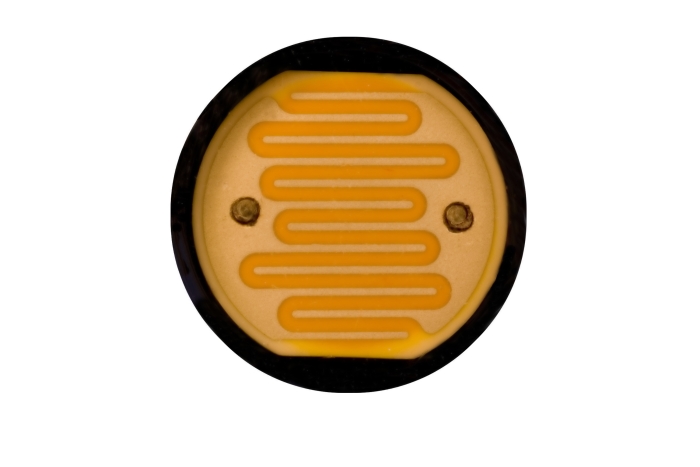

In this image, you can see the surface of a light-dependent resistor.
Thermistor:
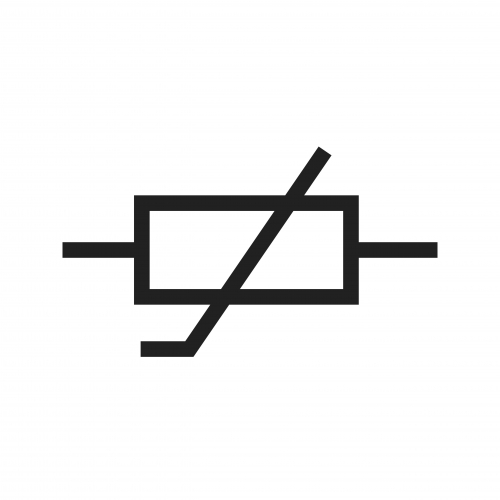
The resistance of a thermistor depends on the temperature of the component. This is useful in circuits related to heating systems in homes.
![]()
Thermistors look quite different to other types of resistors, as you can see in this image.
Now that you have learnt about some of the different types of resistors, let's try some questions!
You can look back at all this information by clicking on the red help button on the screen at any point.








