How does a power station work?
Most of the energy that we use in the home is in the form of electricity. This electricity comes from power stations like the one shown below.
 |
| Power station cooling towers |
A coal power station works by burning the coal. As coal is full of carbon, it contains a large amount of chemical energy and will burn slowly. It will also transfer this chemical energy into heat as it burns. This heat energy is then used to boil water and turn it into steam.
The steam in then forced through turbines, where another energy transfer occurs - the turbines are forced to rotate, converting the heat energy into kinetic energy.
Finally, the turbines are attached to a generator, which is a giant magnet surrounded by coils of wire. The rotation of the magnet inside the coil will induce a voltage - this essentially means that electricity can now flow. So the final energy transfer is kinetic energy to electrical energy.
The thing that all power stations have in common, regardless of whether they are fossil fuel or an alternative resource, is that they force a turbine to rotate a generator, in order to transfer kinetic energy into electrical energy.
.jpg)
In the diagram shown above, the fuel used is coal. Coal is a fossil fuel and stores its energy as chemical energy.
Fossil fuels were formed from dead plants and animals kept under pressure for millions of years. Coal, oil and natural gas are all fossil fuels.
The need for renewable energy
Fossil fuels will eventually run out. On top of this, the burning of fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributes to the Greenhouse Effect and is a contributing factor to Global Warming. Therefore, there is an increasing need to produce our energy from alternative resources that do not release carbon.
You need to be able to compare the advantages and disadvantages of various alternative energy resources. This is summarised in the table below.
| Energy resource | How it works | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Wind | A wind turbine spins as the wind blows and transfers the kinetic energy of the wind directly into electricity, as they contain a generator. | Do not take up a lot of space. The land underneath can still be used. | Unreliable - they do not work if the wind speed is too fast or too slow. |
| Hydroelectricity | Water is stored in a dam. It is made to flow downhill, rotating a turbine attached to a generator. | Can easily control the output of electricity, and can store it for when it's needed. | Increases risk of flooding; destroys habitats. |
| Tidal | The movement of the tides rotates a turbine attached to a generator. | Reliable - tides will always go in and go out every day. | Difficult to repair and can kill fish. |
| Nuclear | Nuclear reactions in a reactor produce enormous amounts of heat. This boils water to turn it into steam. The rest of the process is the same as a fossil fuel power station. | Produces huge amounts of energy from a very small amount of fuel. | Nuclear waste has to be sealed and buried, and then takes thousands of years to safely decay. |
| Solar | Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity. | Produces no pollution at all. | Unreliable - does not work when the sun is not shining. |
| Biomass | Plants and animal waste are burned to turn water into steam. The rest of the process is the same as a fossil fuel power station. | Makes use of waste material. | Releases carbon dioxide when burned. |
Food labels
Let's now think about energy in a different context: the energy in your food.
Food stores its energy as chemical energy. Once you have consumed it, your body will use this energy to transfer it to other forms so that you can move, breathe, and so on.
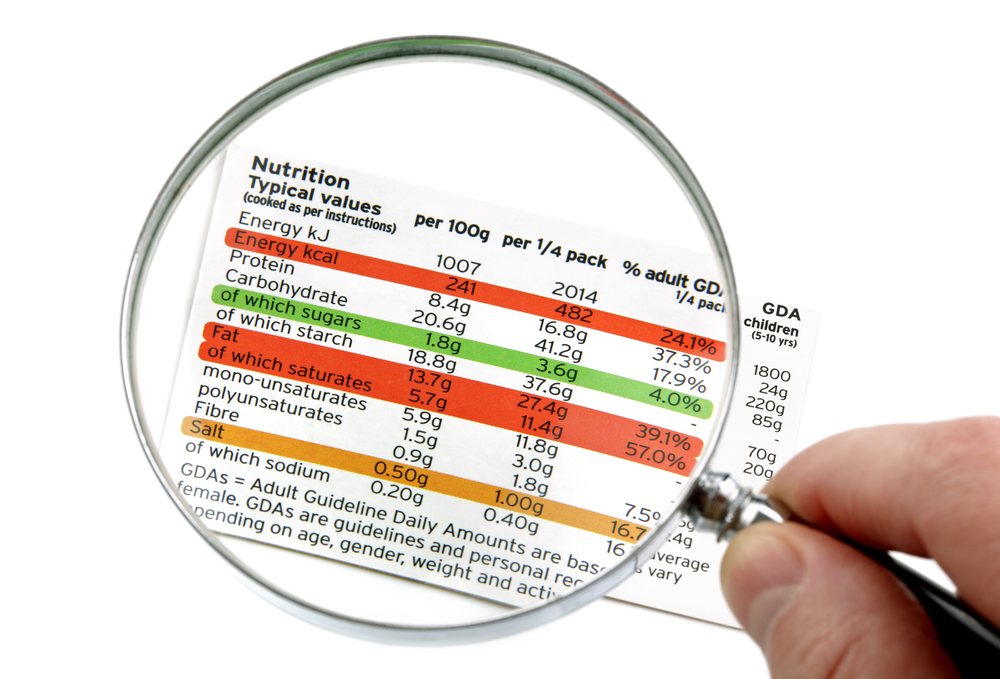
You may have seen nutrition information on food packaging. This isn't just there for people to read if they happen to be interested - it is a legal requirement for food companies to put this information on their packaging. People should consume a specific amount of energy every day, so they must be aware of how much energy is in their food (as well as sugar, fat, and so on), so that they can decide how much to eat, and to work out what foods will provide a healthy, balanced diet.
Energy bills
Finally, let's think about paying for energy.

Every home in the country needs to pay their energy bills to keep their lights switched on and all their appliances working. Energy companies will charge people by the kilowatt-hour (kWh) and work out their energy bill based on how many kWh a household has used. The kilowatt-hour is the amount of energy transferred by 1,000 W of power in 1 hour. To convert W to kW, you must divide by 1,000. Energy companies use this unit instead of the Joule because the amount of energy in Joules would be such an incredibly large number, it would not make much sense.
To work out energy in kWh, you must multiply the power in kW by the time in hours. If you then need to work out a cost of electricity, you need to take this one step further and multiply your answer by the cost per kWh.
Here is an example of a calculation to work out the cost of running a 500 W appliance for 3 hours at a cost of 2p per kWh:
Divide the power in Watts by 1,000 to get kW: 500 W = 0.5 kW
Energy = Power x time = 0.5 kW x 3 h = 1.5 kWh
Cost = energy x cost per kWh = 1.5 kWh x 2p per kWh = 3p.
There's a lot to do there but remember that you can check back to this introduction at any point by clicking on the red help button on the screen.
.jpg)







