Did you know that plants only use about 5-6% of all the water they absorb for photosynthesis? So what happens to all that water anyway? Let's find out more below.
.jpg)
Plants can’t help but lose water continually to the air. This is called transpiration.
Water is constantly lost from the leaves of a plant through pores called stomata. When a plant opens its stomata to allow carbon dioxide in for photosynthesis, water will evaporate and diffuse out of the stomata. More water is drawn up from the stem and the roots to replace the lost water. This is because a concentration gradient exists, there's more water in the roots than the leaves. Water moves via osmosis from a high concentration in the roots to a lower one in the leaves. As water moves from the roots to the leaves, more water is drawn up from the soil into the root hair cells. This occurs because the concentration of water in the soil is larger than in the roots so water moves via osmosis into the root hair cells.
This process is known as the transpiration stream.
Although transpiration is inevitable, it's also quite useful! It helps the plant remain cool and allows minerals to be drawn up the plant along with the water. It also gives plants structure and support.
Factors affecting transpiration
Transpiration is affected by many factors:
1) Temperature - increasing the temperature makes transpiration happen faster, the plant loses more water from its leaves. This is because water evaporates at a faster rate when its warmer.
2) Humidity - if it's really humid it means there's a lot of moisture in the air, the concentration of water outside the plant is higher than inside the plant; the plant doesn't transpire as much so doesn't lose as much water.
3) Wind/air movement - if it's really windy water vapour is blown away from the leaf. The concentration of water outside the plant is higher than inside the plant causing the plant to lose more water from its leaves.
4) Light intensity - if its really sunny, the stomata will open to let in more carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, this causes the plant to lose water.
Plant adaptations
Plants have adaptations that allow it to do a particular job.
Root Hair Cell
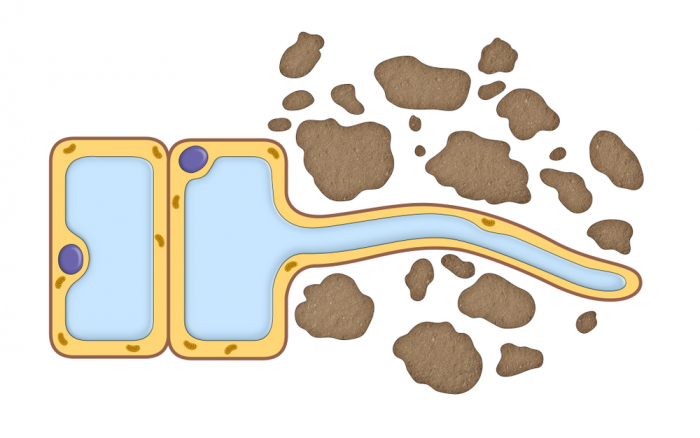
Root hair cells are specialised cells found at the roots of a plant (see image above). These cells are thin and long making them useful to manoeuvre between soil particles in search of water. The large surface area of the root hair cell allows a greater chance of contact with water. Root hair cells contain lots of mitochondria which provides the cell with energy. This energy is essential for active transport needed to take in minerals from the soil.
Stomata
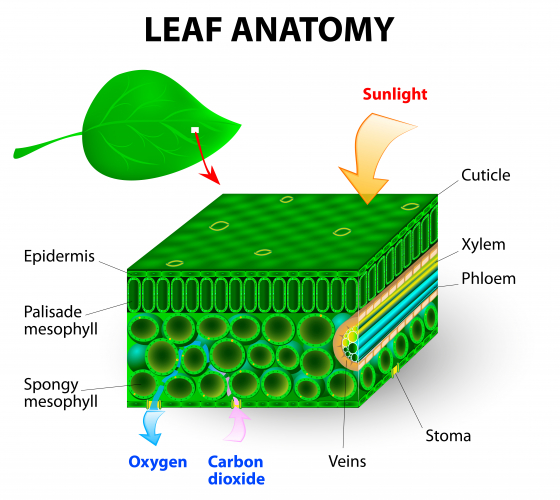
Another adaptation of the plant is found in the leaf of a plant. The lower epidermis layer contains the stomata (stoma for one pore). These stomata allow gases in and out of the underside of the leaf. The stomata are found between guard cells which open or close the stomata depending on how turgid (full of water and swollen - stomata open) or flaccid (lacking water and shrunken - stomata closed) the guard cells are. The stomata will open to allow in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis during the day but will close during the night when there's no sunlight.
Xylem
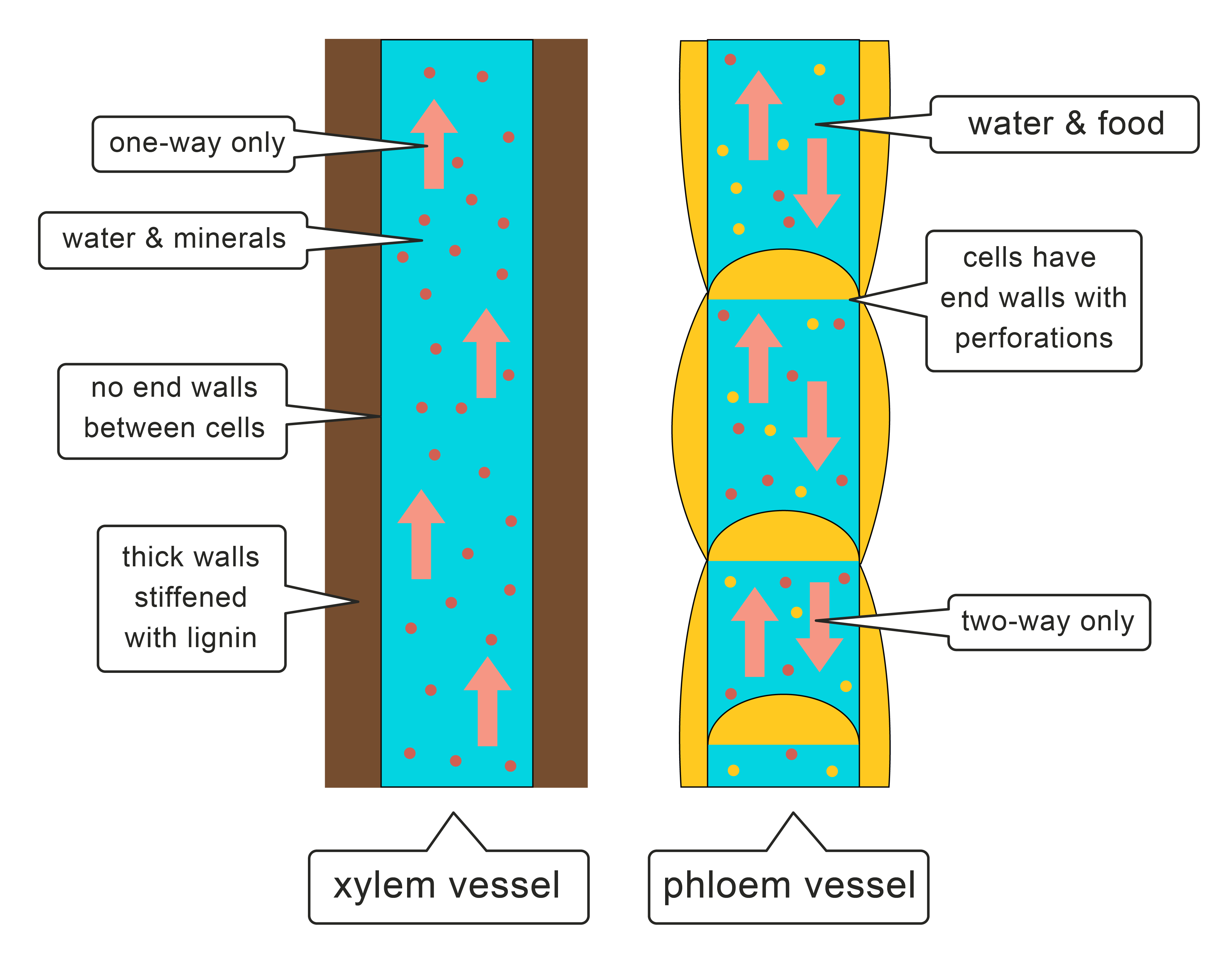
Water moves through xylem vessels. Xylem vessels are a hollow continuous tube that transports water and minerals in one direction from a plants roots to the plant's leaves via the stem. This allows water to travel uninterruptedly up the stem to the leaves. Xylem vessels are made of lignin that strengthen the walls of the xylem vessel. This also helps to support the plant.
Phloem
Another transport vessel the plant has is called the phloem. The phloem vessels move sucrose (a form of sugar) that the plant has made by photosynthesis to where it's needed (for example in growing parts of the plant and storage). Food travels up and down the stem using energy. This is known as translocation.
In the following activity, you will explain how transpiration occurs in plants.








