The oil that is pumped from the ground is called crude oil - before we can do much with it, we need to refine it. To see what that means, and why it's so important, we need to look a bit more carefully at what crude oil actually is.

Crude oil is made of hydrocarbons - molecules containing hydrogen, carbon and nothing else.
The hydrocarbons found in crude oil are a group called alkanes. All alkanes have similar looking structures - here are diagrams of the four smallest ones. You need to know their names, structures and chemical formulas.
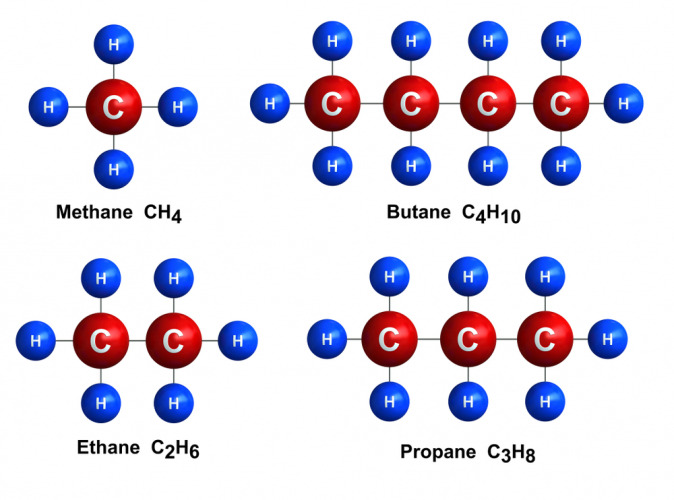
If you look at the structures, you can see how similar the alkane structures are:
All alkanes have a chain of carbon atoms along their middle, called a backbone.
All the spare bonds around the carbon atoms are bonded to hydrogen atoms.
All the bonds in alkanes are single covalent bonds (one pair of shared electrons per bond).
Because of these rules, the chemical formula for all alkanes can be written as CnH2n+2.
n has to be a whole number, but it can be any whole number. The alkanes in the picture are n = 1, 2, 3 and 4, but there are also alkanes with n = 5, n = 20 and even n = 50. If we know the number of carbon atoms in an alkane molecule, we can work out how many hydrogens there must be.
For example: pentane is the alkane with five carbons, so n = 5. We substitute n = 5 into CnH2n+2.
(2 x 5) + 2 = 12, so pentane is C5H12.
Formation of crude oil
Crude oil is a fossil fuel, like coal and methane gas. Fossil fuels are formed from the remains of dead organisms. When small sea animals and plants die, they fall to the bottom of the sea, and get buried in layers of sediments. The layers of sediment gradually turn into rock, sealing the dead remains off from their surroundings. In particular, no oxygen can get to the remains.
As the rocks are buried more deeply, they get hotter and more compressed. The resulting heat and pressure gradually turns them into oil and methane gas. This process happens very slowly - over millions of years.
This means that the oil we use now will not be replaced for millions of years. From our point of view, crude oil is a non-renewable resource - once we use any crude oil, we are not going to get that oil back. That's why we need to be careful how we do use any oil, or other fossil fuels.
Now it's time for some questions.








