Pythagoras' Theorem states that:
In any right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
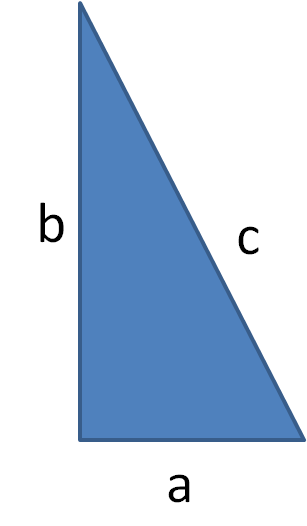
Thus, in the above right-angled triangle: a2 + b2 = c2
Remember that the triangle must be right-angled and that the hypotenuse is always the longest side and the one opposite the right angle.
Example 1
Use Pythagoras' Theorem to calculate the length of the hypotenuse, c, in the following right-angled triangle. Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
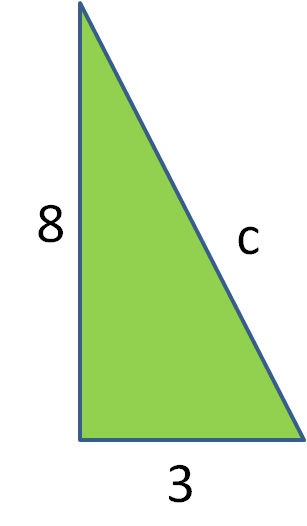
Answer
By Pythagoras' Theorem:
c2 = 32 + 82
c2 = 9 + 64
c2 = 73
c = √73
c = 8.54 (to 3 s.f.)
Example 2
Use Pythagoras' Theorem to calculate the length of the side, a, in the following right-angled triangle. Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
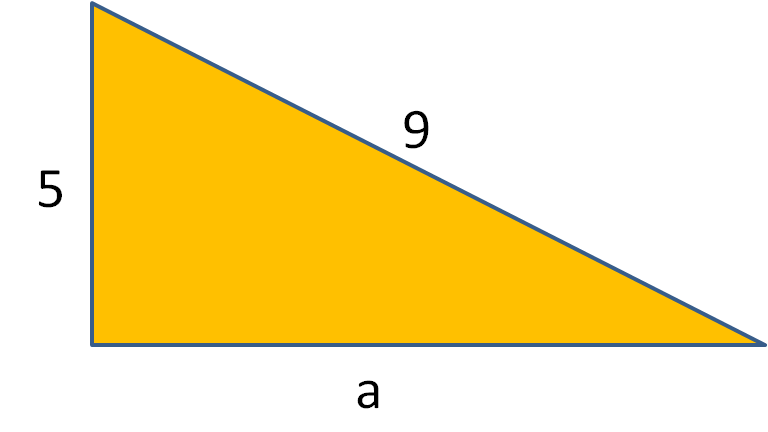
Answer
By Pythagoras' Theorem:
a2 + 52 = 92
a2 + 25 = 81
a2 = 81 - 25 = 56
a = √56
a = 7.48 (to 3 s.f.)
Let's try some questions now.







