We are now going to look at what happens to mass and the number of atoms during physical changes in state and chemical reactions.
A physical change in state is where a substance changes from one state to another, for example from a liquid to a solid.

A chemical reaction is where chemical bonds in reactants are broken and reformed to made new substances.

In both of these, mass is conserved and the number of atoms stays the same.

What do we mean by this?
Let's have a look at the change in state below:
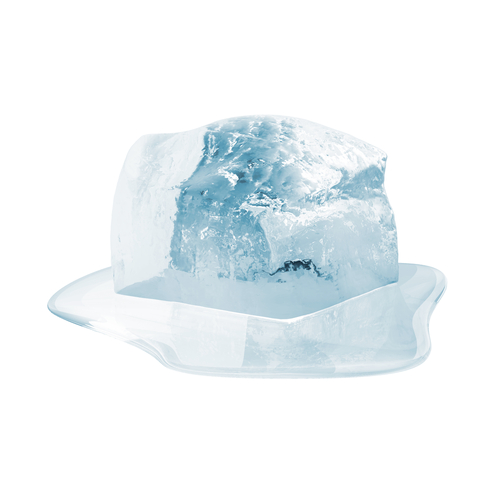

The ice cube is melting, changing state from a solid to a liquid. If the mass of the ice cube in solid form was 14 g, then the mass of the water in liquid form would also be 14 g.
Now let's look at the chemical reaction below:

If you took a piece of potassium and left it to react, it would mix with oxygen in the air, turning it into potassium oxide.
If we measured the mass of the potassium before the experiment and the potassium oxide produced, we could work out how much oxygen has reacted with the potassium.
Potassium + Oxygen → Potassium oxide
15 g + 5 g → 20 g
As you can see, the mass of the two substances before is the same as the substance produced! This is called the Law of Conservation of Mass.

So how is this possible? It's all to do with atoms. When a chemical reaction takes place, atoms in a starting substance rearrange themselves and join back together to form a new substance. In a physical change, atoms rearrange themselves, either getting further apart or closer together. But, the number of atoms will still be the same before and after the reaction.
How do you feel about conservation of mass? Is it all coming together now? Let's try some questions to test your knowledge on changes of state and chemical reactions.