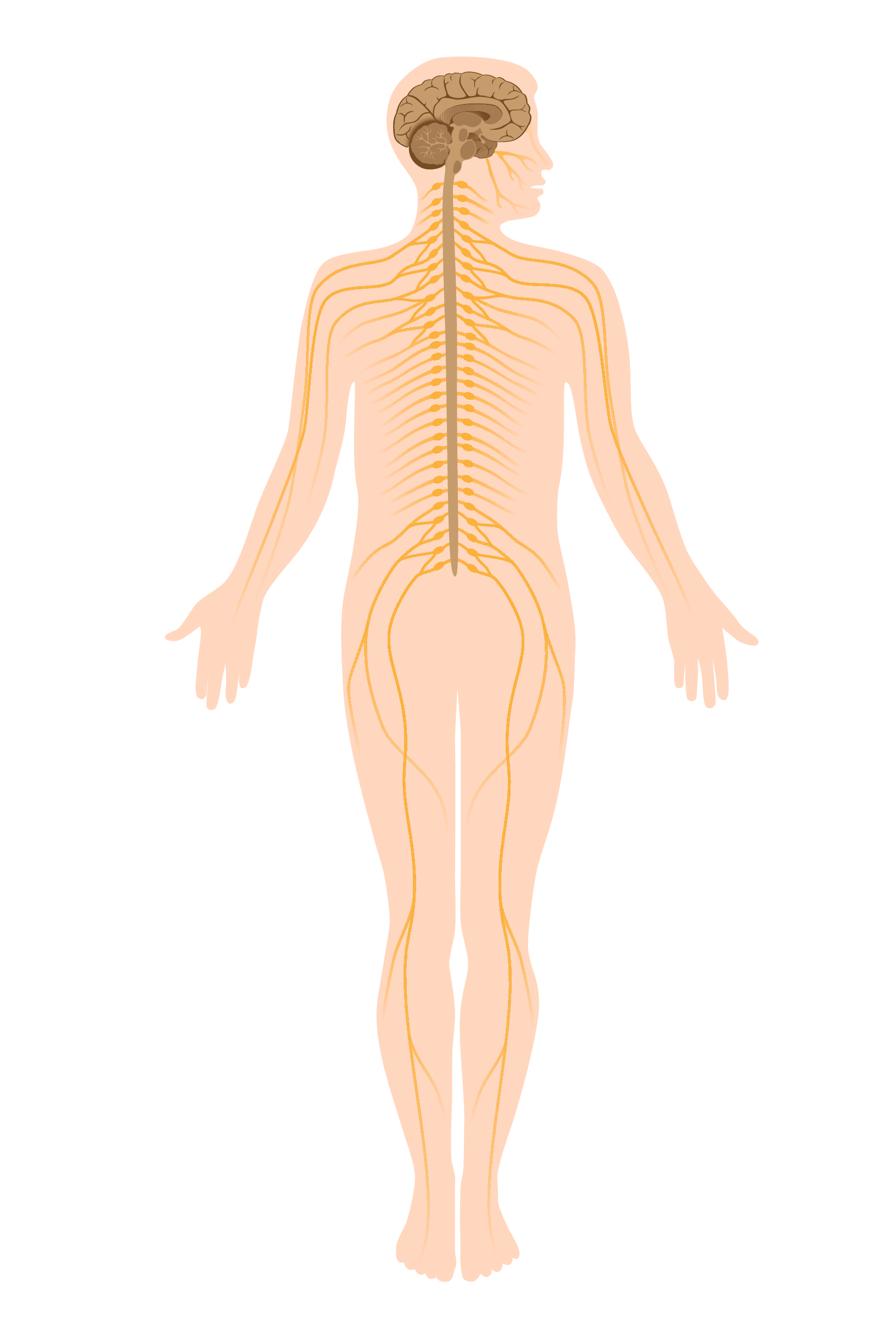
In a previous worksheet on the nervous system, we learned that we need our nervous system to pee! And we also learned that our nervous system consists of nerves and neurones.
A neurone has many special adaptations that allow it to be suited to its function. One of these special features is the myelin sheath. The myelin sheath is a blanket of fatty cells that cover neurones. This helps to protect the nerve cell from damage and really helps to speed up the transmission of nerve impulses. When the myelin sheath is damaged, the nerves can also get damaged and scarred. This makes it harder for the nerve cells to transmit impulses, which can lead to weakened muscles, coordination issues and even paralysis.
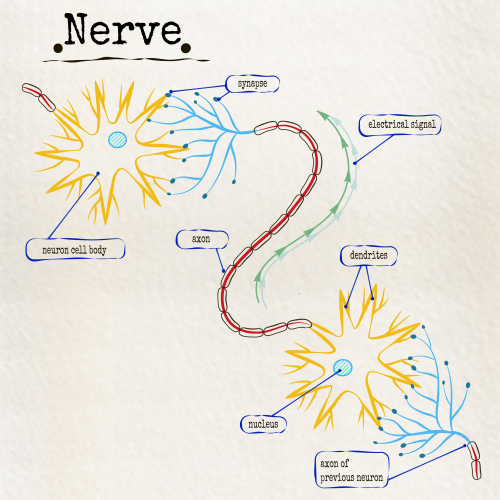
Neurones don't actually touch. Where neurones meet, there is a gap called a synapse. It's here that a specific chemical, called a neurotransmitter, passes on the impulse to the next neurone in line.
.jpg)
Let's have a look at this process in more detail below:
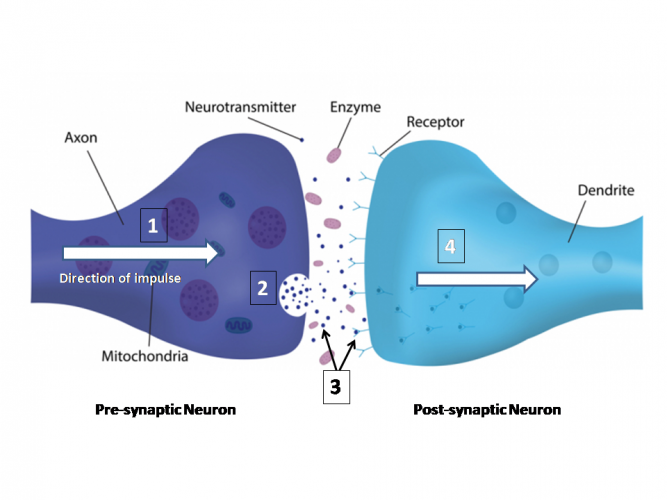
1. A nerve impulse arrives at the synapse of the first neurone, called the pre-synaptic neurone.
2. Neurotransmitters are found in a structure called synaptic vesicles - they are released from the vesicles into the synapse.
3. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse and binds with a receptor on the membrane of the second neurone, called the post-synaptic neurone.
4. The binding of the neurotransmitter and receptor stimulates the impulse down the post-synaptic neurone.
Once the impulse has been passed along, the neurotransmitter is released from the receptor, where it's often degraded by enzymes or taken up again by the pre-synaptic neurone - ready to be used again!
Some drugs can affect the transmission of nerve impulses and the neurotransmitters involved. For example, ecstasy can increase the release of certain neurotransmitters, causing mood-enhancing effects. Caffeine also increases levels of certain neurotransmitters which give feelings of pleasure.
In the following activity, you will be exploring the function of synapses.