
Now, who doesn't love a slice of chocolate cake?!
Unfortunately, around 4 million people in the UK have to be cautious when consuming food with lots of sugar in, like chocolate cake. Let's find out why below:
Glucose is the name given to sugar that's used by the body for energy. The amount of sugar in our blood has to be monitored - sometimes you will have too much and sometimes too little.
The amount of glucose can be affected by:
Eating which causes glucose levels to rise.
Vigorous exercise which causes blood glucose levels to drop.
The monitoring of glucose levels is an example of homeostasis. That's because the body has to keep a constant internal environment. Homeostasis allows the body’s cells to work at their optimum, meaning in conditions that allow them to work at their best.
The conditions of the environment are always changing. Our body has to respond to these changes, but at the same time ensure that certain internal conditions don't vary too much, otherwise, damage could be caused.
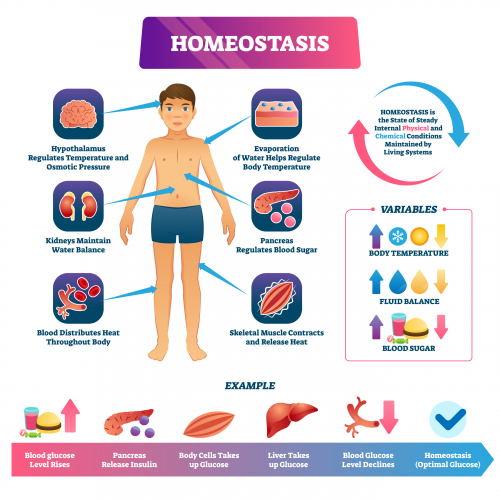
Glucose is monitored and controlled by the pancreas. The pancreas produces different hormones in response to the levels of glucose.
Insulin is a hormone that's released when blood glucose levels are high. It binds to receptors on cell membranes that cause cells to take in glucose - this glucose is used for respiration. Excess glucose is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
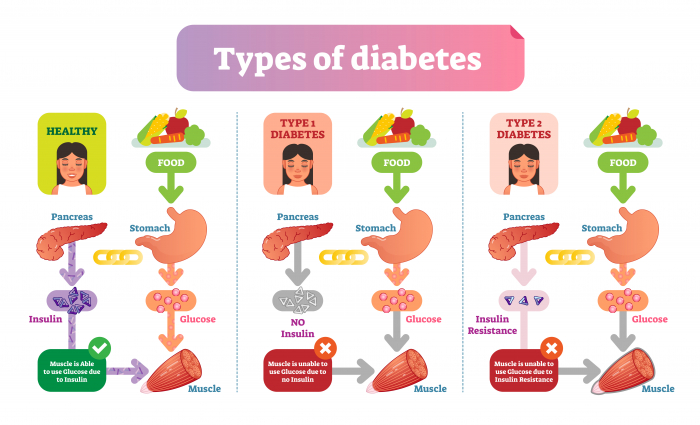
Diabetes is a condition where blood glucose levels aren't maintained - they can get super high, or low and cause all sorts of issues. There are two types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
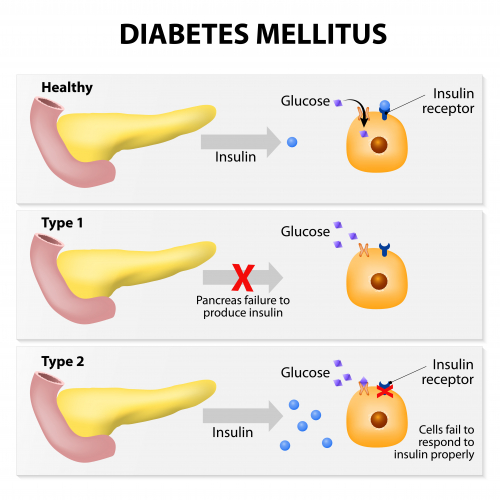
Type 1 Diabetes:
The pancreas doesn't produce enough of the hormone insulin.
Blood glucose levels are uncontrollably high.
It is treated with insulin injections.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Insulin is produced but liver and muscle cells no longer respond to it.
People who are obese are at risk.
It is controlled by limiting simple carbohydrates in the diet, as well as taking more exercise.
By controlling the types of food they eat, diabetics are able to regulate how much sugar is released into the blood through digestion.
Regular exercise means that glucose in the blood will be utilised by cells for increased respiration (which means more energy), this will lower blood glucose levels. This helps diabetics to regulate their blood glucose levels.
In the following activity, you will explain how the body controls the levels of glucose in the blood.








