When we throw a coin and roll a die, how many possible outcomes are there?


We can organise the outcomes using a table:
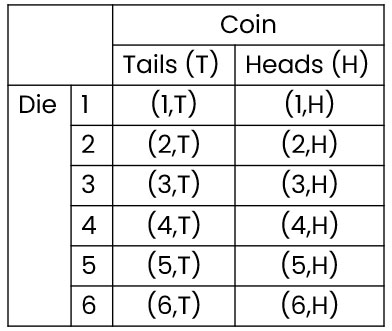
We can see that there are 12 possible outcomes for these combined events (i.e. multiple events occurring at the same time).
The set of all outcomes is called the sample space.
But is there a faster way to find out the number of items in the sample space?
Yes, there is!

A coin has 2 possible outcomes and a die has 6.
We can get how many possible outcomes there are for both the coin and the die by multiplying the number of possible outcomes for each:
2 x 6 = 12
Which is what we got by listing them before!
Let's say we are now throwing two dice and recording their sum.
Each die has 6 possible outcomes.
So the number of all possible outcomes is:
6 x 6 = 36
Can we see how that is so much faster than listing them all?!
.jpg)
Sometimes it is useful to generate the whole sample space though.
In that case, a table is generally what we would use so as not to forget any outcomes!
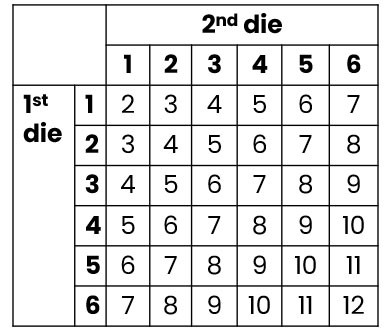
Ready to have a go at some questions?!








