Have you ever played with a slinky?

These toys can be stretched out and their shape will change as a result. What causes this is the force that you apply to the slinky. Let's learn about how forces can affect the shape of different materials!
Forces impact objects in different ways. They can make objects change their speed, or change their direction. But forces can also affect the shape of objects. This is called deformation.
Here is an example: You take an empty plastic bottle, and apply a force to it to squash it so it will fit in a recycling bin.
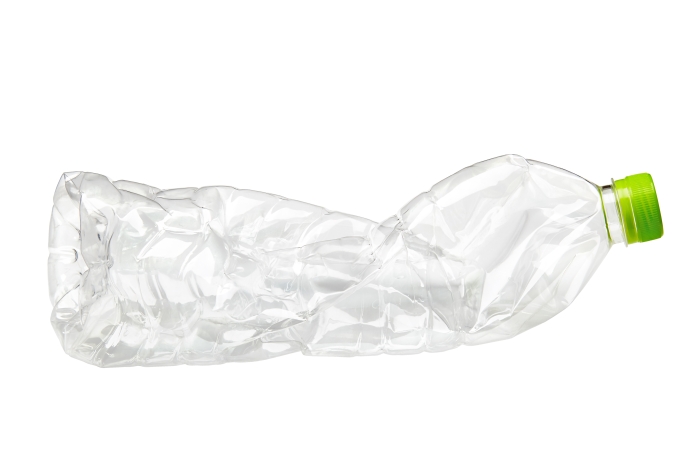

The force you applied caused a deformation in the bottle.
To be specific, when a force squashes an object, we call that compression.
If you take that slinky from earlier and pull on both ends, you are causing another deformation. This time, because you are applying a pull force to stretch the object, you are causing tension in the slinky.
The slinky might start at a length of 20 centimetres. When you stretch it, it might have a new length of 50 centimetres. That means that the slinky has an extension of 30 centimetres - extension tells us the amount something stretches.

These have all been large-scale examples so far, but forces causing compression can affect the bonds between particles! Let's look at how that works.
Imagine you are sitting in a plastic chair. You aren't falling through that chair - why?
You might remember that the chair provides a normal reaction force, acting upwards against your weight. So what's the link to compression?
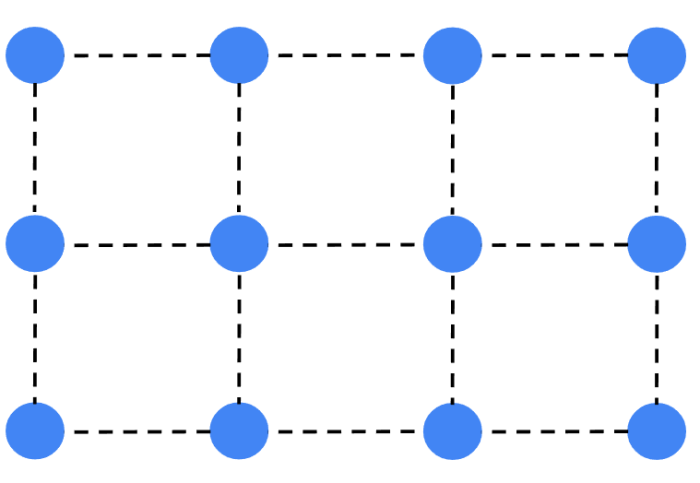
This is a simple diagram showing what the bonds might look like between solid particles. The particles in a solid are arranged in a regular pattern and the bonds between the particles are strong.
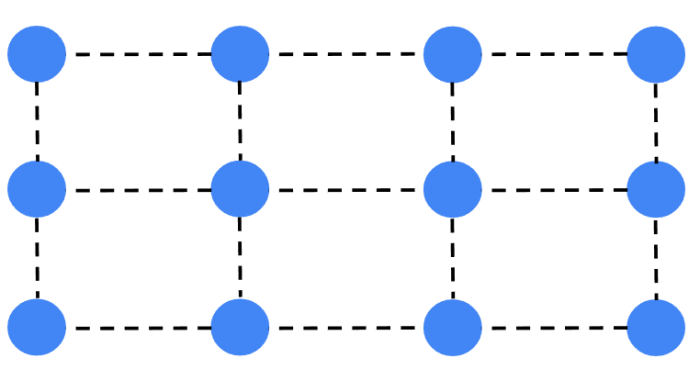
Imagine sitting on that solid surface. When you do, your weight acting downwards pushes the particles in the solid a little closer together. This means that the bonds themselves are compressed, a bit like in the image below.
Here, the particles themselves are the same, but they are closer together. The force you exert on those particles is pushed back and supports your weight in that chair.
This all happens on such a small scale that you can't always see it happening.
Now that we understand how forces can cause deformation, let's try some practice questions!