Mixtures can be separated by physical processes. As these processes do not involve chemical reactions, no new substances are made.
One such process is called crystallisation.
Crystallisation can be used to obtain cystals of a salt from a solution, such as copper sulfate crystals from copper sulfate solution. It involves slowly heating the solution to evaporate the solvent, leaving solid crystals behind.
Step 1
A solution is placed in an evaporating basin and heated with a Bunsen burner.
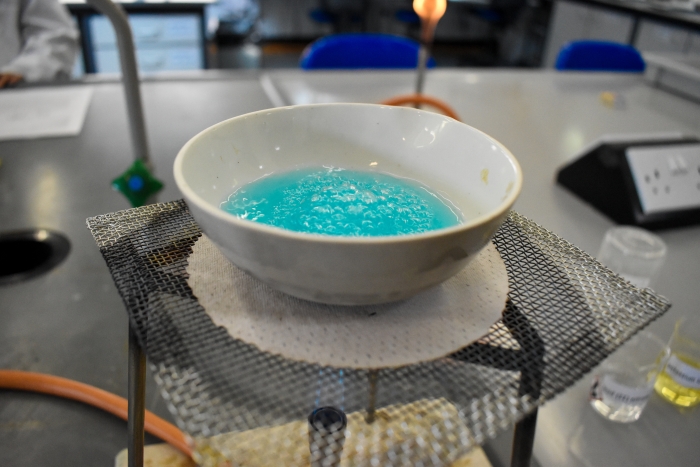
Step 2
When the solution is warmed, some of the solvent evaporates leaving some crystals behind in the bottom of the basin.
Step 3
Stop heating when crystals begin to form around the edge of the basin and about half of the solution has evaporated.

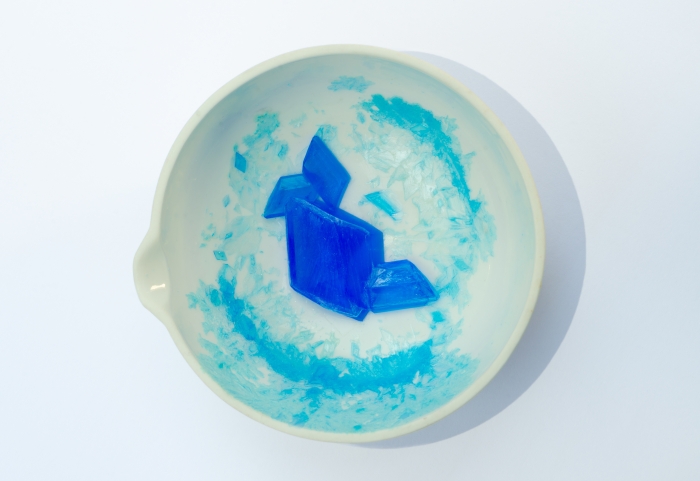
Step 4
Leave the solution to cool down, allowing the remaining solution to evaporate slowly.

Step 5
Dry the crystals using a warm oven or by patting them with filter paper.

You will be left with beautiful blue crystals of copper sulfate!







