Ionic bonding works brilliantly when a compound has a metal and a non-metal in it. The metal atom loses unwanted electrons, the non-metal takes electrons it does want, and everything works well.
What if there isn't a metal and a non-metal? We need other types of bonding - covalent bonding happens between two non-metal atoms.
It's easy to mix up ionic and covalent bonding, so watch out for the ways in which they are similar and different.
A lot of very important substances are covalently bonded, so make sure you can remember the names and formulas of these ones:
| Name | Formula |
| Water | H2O |
| Ammonia | NH3 |
| Methane | CH4 |
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 |
If both atoms are non-metals, there isn't a source of spare electrons to complete electron shells, so ionic bonding can't happen.
For example, imagine having two fluorine atoms. Each atom has seven out of eight positions filled in its outermost shell, and neither atom is going to give up any of its electrons. To solve this problem, the two atoms share one electron each.
The shared electrons sit in parts of the shell between the two atoms. A tiny fairy sitting in the middle of each atom would see a complete outer shell, but this only works if the two atoms are exactly the right distance between each other, making a bond between the atoms. This type of bond is called a covalent bond, and we can draw a dot-and-cross diagram for this sort of bonding as well. The covalent bond is the part where the circles touch or overlap.
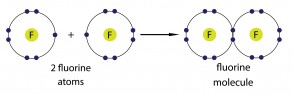
In this diagram, only the outermost shells are shown, but it's usually easier to work out the dot and cross diagram by drawing all the shells.
You can do the same thing with compounds. Carbon dioxide is carbon and oxygen, and they are both non-metals. Carbon needs another four electrons, and oxygen needs another two. To make carbon dioxide, each bond between carbon and oxygen has two electrons from the carbon and two from the oxygen. If you look round each oxygen, they both seem to have eight electrons, and if you look round the carbon, it seems to have eight electrons.
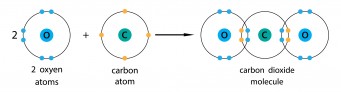
Be really careful not to mix up the different dot-and-cross diagrams.
Remember:
If it's a metal with a non-metal, you have ionic bonding. One or more electrons move to the non-metal, but the atoms stay separate.
If it's a non-metal with a non-metal, you have covalent bonding. Some electrons are shared, so the atoms are drawn touching or overlapping.
Let's move on to some questions now.








