The picture shows part of the Earth in a satellite image with the atmosphere as the illuminated blue line surrounding it.
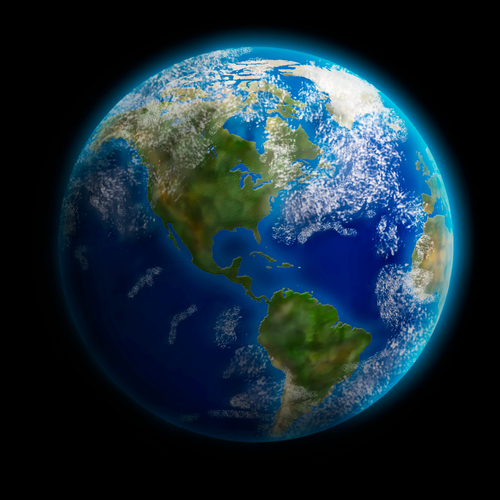

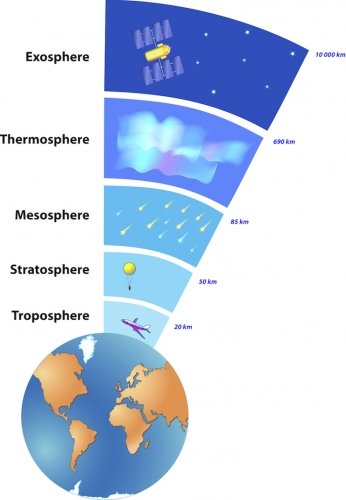
The Earth's atmosphere contains air particles, as well as water particles which form clouds. It is a layer of gases that are retained by the Earth's gravity. The atmosphere is made of several layers shown in the diagram below. The layers in the image are not to scale with the image of the Earth. Their real dimensions are labelled in the diagram.
It is believed that the early atmosphere was formed mainly by gases emitted by volcanic activity. These gases were carbon dioxide, ammonia, water vapour and methane. Oxygen was totally absent or very limited. When the Earth cooled down, water vapour condensed and formed the oceans.
Only bacteria could live in an oxygen-free environment; bacteria were the very first form of life on Earth and the first organisms that developed photosynthesis. Later on, plants further added oxygen to the atmosphere so more complex organisms evolved.
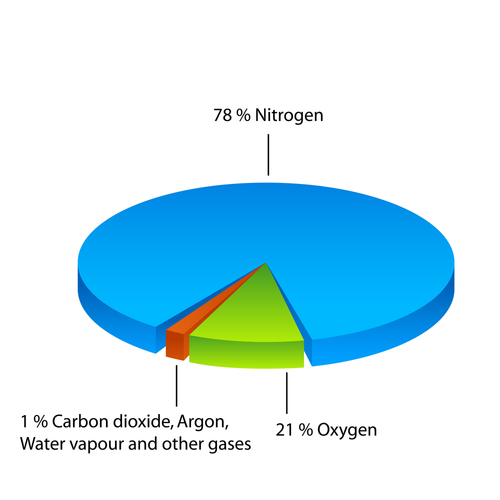
The composition of the atmosphere today is shown in the diagram below:
Unfortunately, human activity is constantly altering the Earth's atmosphere with pollution. The consequences will be devastating:
Soot is incompletely burned carbon from the burning of fossil fuels. It coats leaves, reducing their ability to photosynthesise. Soot is also harmful for humans to breathe, leading to an increased risk of bronchitis and lung cancer. It mixes with snow in the Arctic areas and causes melting of the ice.
Combustion (burning) of fossil fuels pollutes the air with carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide. Sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen dissolve in water in clouds and form acid rain. Acid rain causes breathing problems, damage to trees and erosion of buildings. Carbon dioxide and some other gases are called greenhouse gases. They trap heat from the Sun in the atmosphere, which leads to global warming.
Smog is formed when smoke particles mix with fog. Smog is a major problem in large cities and damages the lungs.
CFCs produced by aerosols and refrigerators damage the ozone layer, which protects the Earth from ultraviolet radiation, leading to an increase in skin cancer.
Let's have a go at the questions now and see if we can identify some positive things that can be done to reduce these problems.








